This site is under construction! Stuff be missing, beware! Contribute!
If you have additions, corrections or concerns, open an issue or contact a maintainer.
Voice Map is released! See here for a giant map of (almost) all voice characteristics and pedagogy!Table of contents
Glossary
Below is a list of voice related words and the concepts relating to them, links and definitions where available.
Sound Production Related
Glottal Behaviour
- covers all behaviours to do with phonation / sound production
- vocal weight, pitch, closure, FVF, subglottal pressure, onsets, and even some microbehaviours are all under this umbrella
- a catch all term for how the voice is produced and how ‘cleanly’ it is produced
- has a lot to do with clarity and tone purity or HNR
Vocal Weight
- how ‘heavy’ the voice sounds
- doesn’t take into account volume, pressed phonation, breathiness
- Vocal Fold Vibratory Mass is likely the underlying cause of the sound
Vocal Fold Vibratory Mass (VFVM)
- how much of the vocal folds are actually vibrating during phonation
- when more vibratory mass is involved, we get more surface area creating sound waves, and likely this will increase closed quotient
Volume
- the loudness of a voice
- usually from airflow-closure more than vocal weight or pressed phonation
Quotient
- measurement of how long it takes for the vocal folds to open vs how long it takes for them to close
- used in research because it’s objective and it’s a good but not perfect correlation to vocal fold vibratory mass / vocal weight
- usually measured using EGG / electroglottography
Open Quotient
- related to low vocal weight
- how long in each glottal cycle (each flap of the folds) the folds are opening
Closed Quotient
- related to high vocal weight
- how long in each glottal cycle (each flap of the folds) the folds are closing
Pitch and Range Related
Pitch
- the fundamental (F0) frequency of the voice
Base Pitch
- the pitch a voice naturally returns to after intonation
- defined by vocal weight / fold mass due to the connection between fold mass and pitch
- the common return to point or anchor or home position for a voice
Phonate
- verb: to produce a tone / pitch by making the vocal folds vibrate
- requires both closure (adduction) and airflow
Register
- see below
Laryngeal Vibratory Mechanism
- describes how and how much of the vocal folds vibrates
M0 - Vocal Fry
- also known as
- pulse
- strohbass
- fry
- is at the bottom of your range
- sounds like an idling motorcycle
M1 - Modal voice
- your normal speaking register
M2 - Falsetto / Head Voice
- high pitch, often hollow register
- can be made less hollow with with slightly adding vocal weight
M3
- whistle register
TA Muscles
The following is assuming TA muscle is the thing responsible for what we see, but it could be something else in which case replace TA with whatever is actually doing the work. TA seems to be involved though and it’s unlikely to be anything else.
- thyroarytenoid muscles, running the length of the vocal folds
- more activation ~= more weight
- can make M2 sound more full and be more stable and bright rather than the “too thin” or hollow quality M2 often has, when used with sufficient closure
- can help with more general (not breath specifically) support to the voice to make it more robust
- can blend m1 and M2 to avoid breaks and more reliably come back into m1 from a slide
- a component of “shouting posture”
Resonance Related
Resonance
- is a filter, which highlights frequencies in the voice
- changes the timbre or non-pitch qualities of a voice
- is dependent on the size and shape of the vocal tract
- the size of a container is its external volume, space is the internal volume and resonance is how sound is affected by the volume and shape of that space
Vocal Size
- do not try to change the size of your voice intuitively or without proper exercises / guidance unless you know not to constrict or use extraneous muscles!
- a perceptual quality of voice, which describes the total effect of all resonance modifications
Brightness
- the amount of high frequency harmonic information in the voice
- a perceptual quality caused by the amount of high frequency harmonic information
- a high resonance voice can sound dark due to muting effects like nasality and breathiness
- clarity, vocal weight and twang are the main factors that allow resonance to highlight upper frequencies, allowing for brighter tone
- the frequency of formants, particularly F1, essentially resonance (outdated)
Larynx
- houses the vocal folds
- can be raised to get a brighter sound
- the ‘adam’s apple’ is outside of the thyroid cartilage, part of the larynx
Embouchure
- loosely describes how resonance changes in the mouth
- affected by macrovowel
Macrovowel
- the use of a vowel shape to color speech
- keeping the mouth in the same position / posture as a certain vowel when speaking
Microvowel
- to modify individual vowels to be darker or brighter without changing how the vowel is interpreted
OPC, Oropharyngeal Closure
- raises resonance by decreasing the width of the back of the mouth
- affects formants F1 and F2
- associated with loli voice and some “anime” voices, hyperfem, “small” voices
Twang, AES constriction
- at the cost of buzziness (not vocal weight), adds the impression of high resonance
- increases the impression of brightness
- seen in some country singers, some Australian accents
- often induces hypernasality
Formant, F1 F2 or R1 R2 etc
- these are resonance peaks in the voice, caused by the shape of your vocal tract
- the ratio between F1 and F2 largely determines vowel
- F1 is the first formant and is often altered through larynx height and OPC
- F2 is the second formant and often altered through mouth space
- F3 is from the difference in size between the mouth and the space between the teeth, mostly between the teeth and tongue
- F4 is from the same but lips
Clarity Related
FVF, False Vocal Folds and constriction
- “white noise” quality in background is louder and may be present even when not breathy
- increased subharmonics
- sometimes a “rattle” like quality is heard, which is essentially really high frequency harmonics up around 10kHz
- bad for vocal health in the long term
Subharmonics
- rough quality similar to creak/fry
- extra harmonics appear; one in between each harmonic, essentially making it as if the pitch was halved
- this is due to every 2nd cycle of the vocal folds being interrupted
- it’s also possible for it to cancel out every 3rd cycle instead, leading to two extra harmonics instead of just one
- theoretically there’s no limit to the fraction of cycles interrupted as long as it’s consistent
- can be a sign of slight FVF constriction interfering
- on subharmonics
Harmonic to Noise Ratio (HNR)
HNR is the description of essentially how noisy a voice is. We have harmonics - which are the horizontal lines in the image - and then there’s noise in between, either from constriction, breathiness or a combination. You can see in the image how there is a clean looking pattern on the left, and a noisy one on the right. This could be called the ‘clarity’ of the voice, though it refers specifically to noise and not things like nasality or knodel effects which might make a voice sound ‘out of place’.
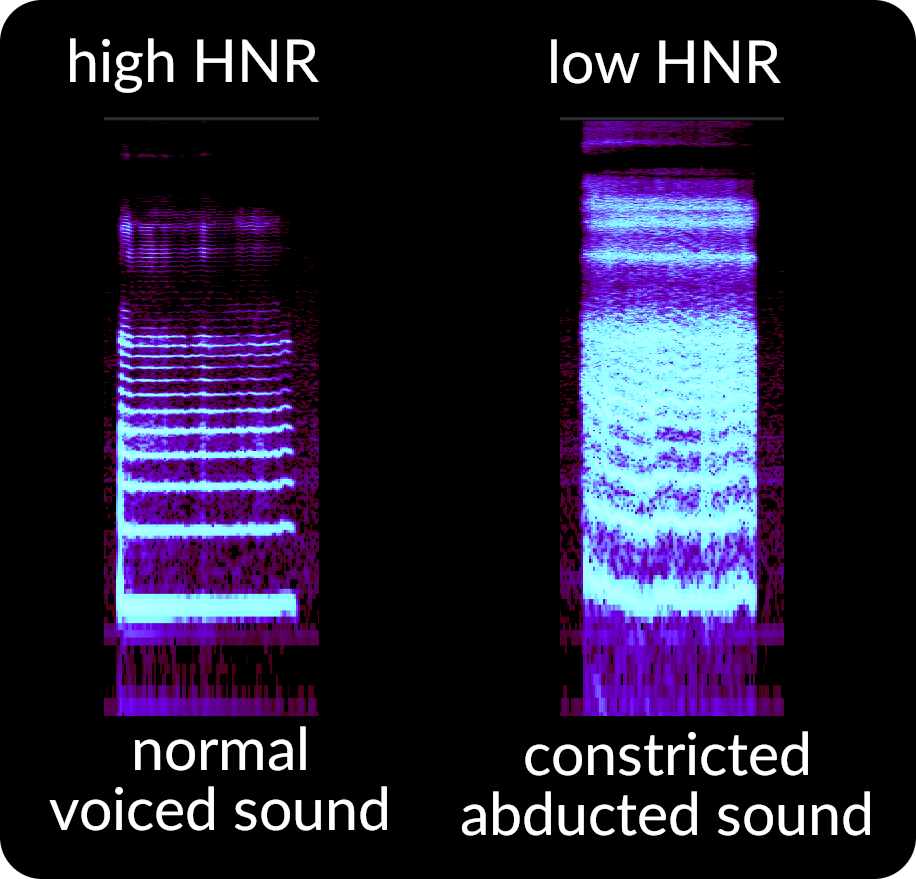
Primary sources of low Harmonic to Noise ratio: ・abduction (breathiness) ・FVF constriction ・vocal fry and creak
Exercise and Training Related
SOVTEs, VFEs
- Semi Occluded Vocal Tract Exercise and Vocal Function Exercises
- helps give a baseline for airflow and glottal behaviour to an extent
- helps warmup and warmdown the voice to help with vocal health and fatigue
- can show if there are any voice related problems
Breath Support
- low support voices are typically unstable and fluctuate in pitch uncontrollably, may flip between m1 and M2 unpredictably
- high support voices are more robust
- putting a fair bit of pressure into the /s/ sound can induce better support
- M2 and quiet voices tend to be low in support without training
Cover Related
Cover
- hides or restricts a certain aspect of voice, usually fullness or resonance
Tongue Root Retraction
- has a goofy, dark sound
- associated with Meatwad, Stitch
- can sometimes happen unintentionally when doing OPC
Hypernasality / Nasality
- too much passage of air through the nose when phonating
- darkens the sound and works as an antiformant
- makes F1 and F2 almost nonexistant
- can make vocal weight less prominent at higher pitches
- nasal sounds should be the only muffled sounds when the nose is pinched, so you can read ?non-nasal passages to test for it
Hyponasality
- too little passage of air through the nose when phonating
Speech Pattern Related
Intonation
- the changing of pitch to add color to speech
- intonation range is how far we intonate / change pitch in speech
- intonation frequency is how often we change pitch in speech
Tempo
- how much we change the speed of speech where some words are slowly spoken and some are rushed past
- how fast in general the speech is
Emphasis
- making a single sound or word stand out in speech
- this usually relates to the use of volume for emphasis but can also be used in other ways
- emphasis can be from volume, intonation, tempo
Resonance Fluctuation
- how much the resonance changes through speech, or how much it is linked to pitch
- some resonance fluctuation is normal
- more resonance fluctuation is more dynamic and sometimes sounds out of place
- no resonance fluctuation can sound unnatural
Articulation
- how and how much the mouth moves in order to form vowel sounds
- under vs overarticulated can sound like the difference between “uh muh guhd” and “ouw maiy gaud”
- this can be used to emphasize things, or for generally making the voice more expressive
- since it deals with how the mouth moving, a subset of this is mouth space as a resonance and brightness modifier
Anatomy Related
Vocal Tract
- the mouth, nose, larynx and pharynx; everything from the larynx up
Thyroarytenoid muscles
- lowers pitch
- adds weight (probably)
- can be used to make M2 more full sounding
- if deactivated, results in a hollow, M2-like, dark sound
Cricothyroid muscles
- raises pitch
Thyrohyoid muscles
- raises the larynx to the hyoid bone
- usually activates when raising pitch, resulting in pitch/resonance conflation
Stylohyoid muscles
- raise the hyoid bone (and therefore larynx) toward the base of the tongue
- can be activated when consciously raising the larynx
Vocal Ligament
- the vocal folds, without the muscles
Vocalis muscle
- thyroarytenoid muscle
- [needs disambiguation]
AES/Aryepiglottic Sphincter
- associated with twang
- when the epiglottis is moved to make the passage in the throat smaller and cause a high frequency filter
- it being responsible for twang is contested, but generally high closure plus AES constriction does result in the twang sound quality